|
|
 |
|
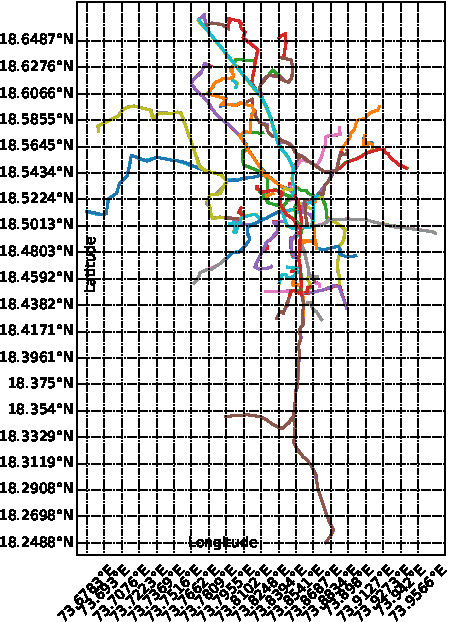
These routes are further analyzed to identify the extent of overlap of routes. It is identified that there are 11 sets of routes with more than 80 % overlap.
|
 |
|
|
 |
|
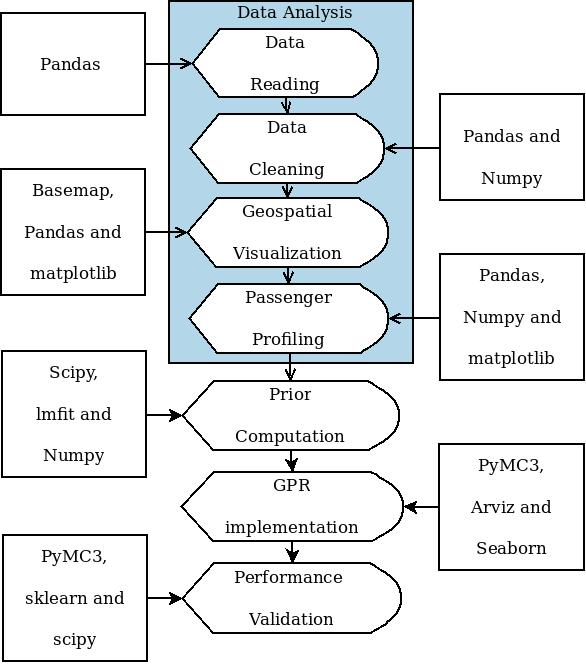
The prediction process using GPR is published as a journal paper
|
 |