|
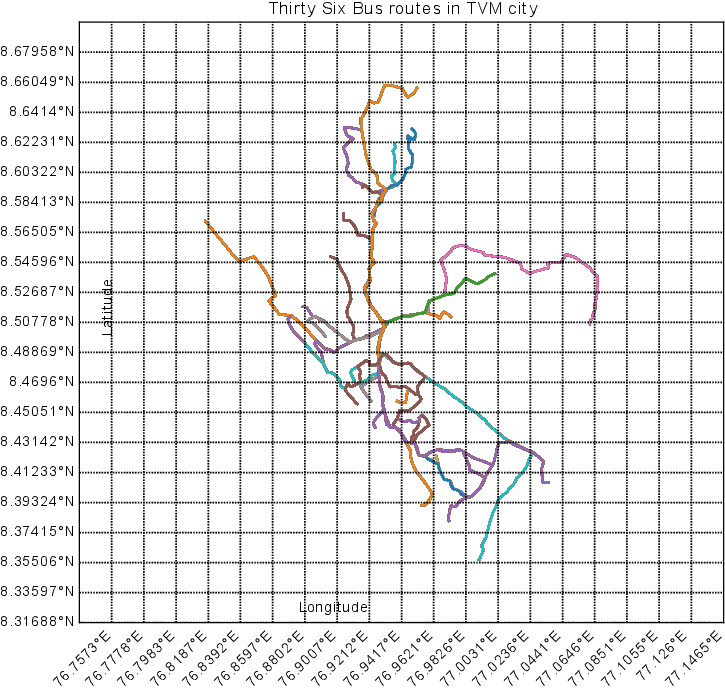
This proposal broadly aims at the adaptation of technology to improve the operation of KSRTC bus routes so that theearning per km is maximized and the reliability of operations is ensured. A pilot project was implemented for Kerala State Road Transport Corporation (KSRTC) to analyze the routes in terms of the revenue and the passenger traffic and
|
 |
|
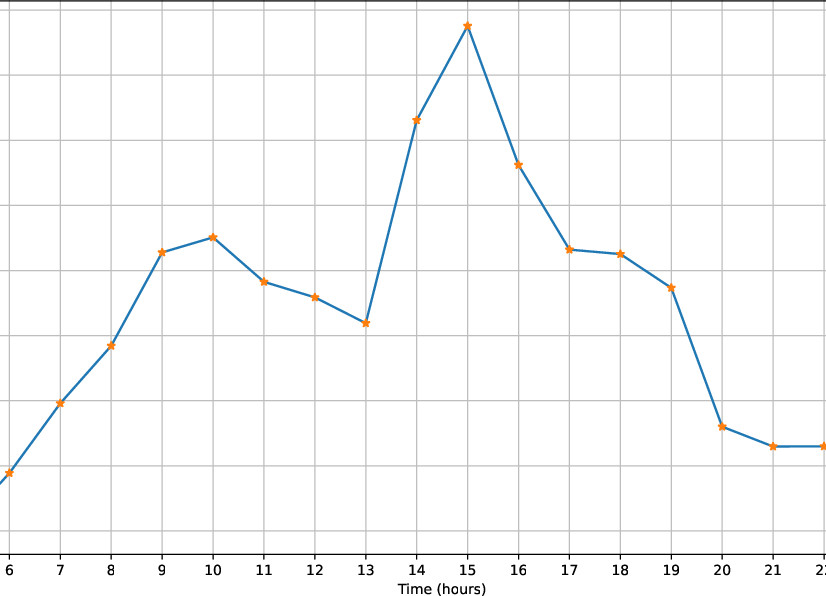
The passenger traffic of selected routes over nine months is averaged and plotted to study the traffic model.
|
 |
|
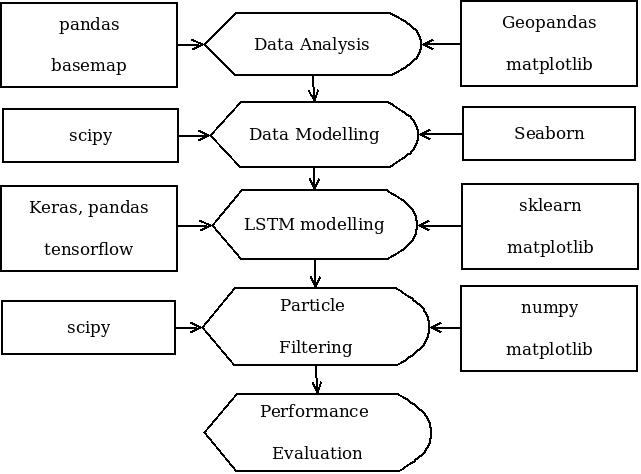
This work is published as a journal paper
|
 |